All living organisms can be grouped into two types based on their fundamental cell structure. They are prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and the cells they possess are called prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells.
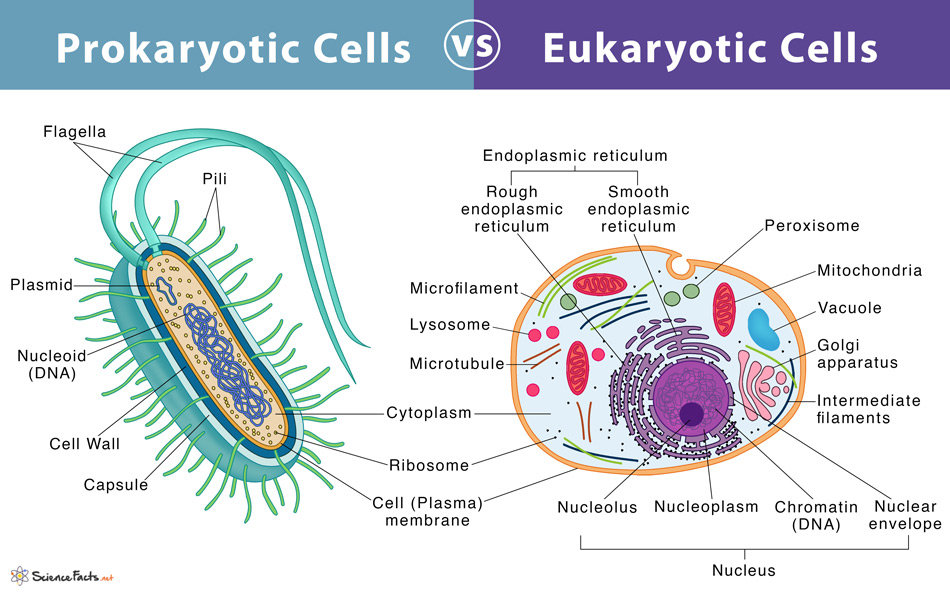
Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes are primitive organisms lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. The term ‘prokaryote’ is derived from the Greek words ‘pro’, meaning ‘before’ and ‘karyon’, meaning ‘kernel’. Together it means ‘before nuclei’. In contrast, eukaryotes are advanced organisms with a well-defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. The term ‘eukaryotes’ is derived from the Greek words ‘eu’, meaning ‘good’ and ‘karyon’, meaning ‘kernel’, meaning ‘true nuclei’. The eukaryotes are thought to have originated from the prokaryotes about 2.7 billion years ago.
Compare and Contrast Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Although they share some common characteristics, prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in most aspects, such as cell size, shape, organization, and life cycle, including reproduction. The main differences are given below.
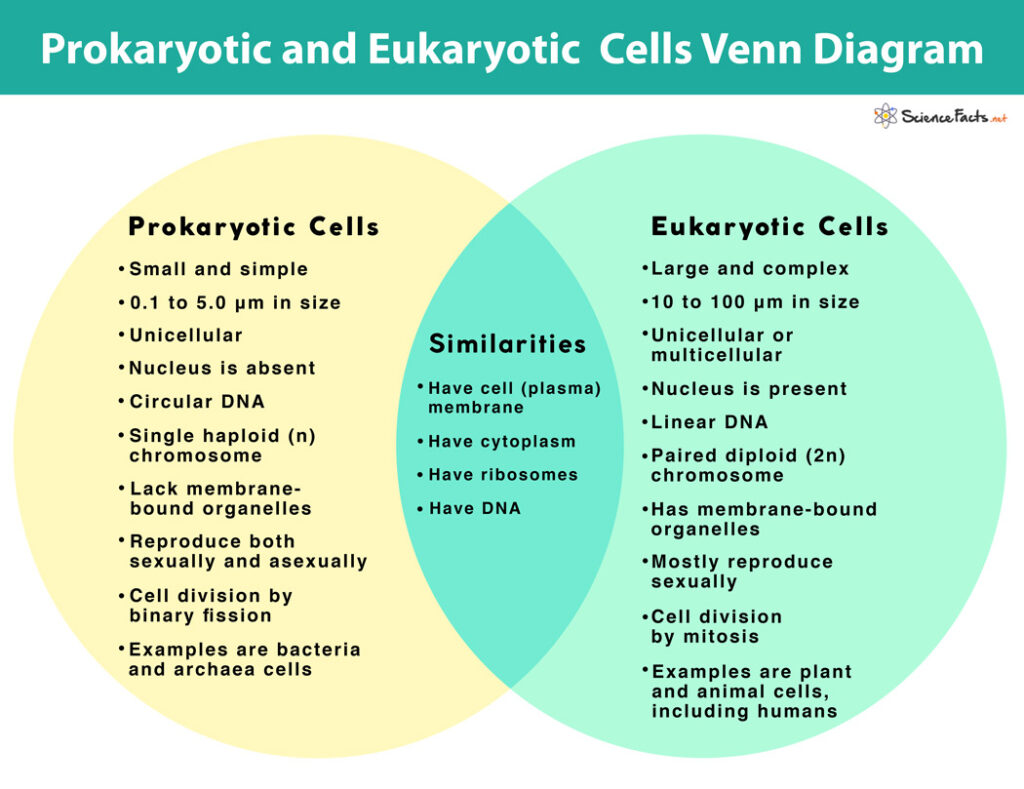
Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes Venn Diagram
What is the Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
What do Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have in Common
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are alike in some ways and share some common features that are given below:
- Plasma Membrane , an outer covering that allows selective entry and exit of substances in and out of the cell, is found in both cell types. Their fundamental composition in forming a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins is also the same.
- Both contain cytoplasm , a jelly-like fluid that fills the cell’s entire interior, where all other cellular components are found.
- DNA is the genetic material in both cell types.
- In both, ribosomes help in protein synthesis.
Ans . Viruses are not cells and thus are neither a prokaryote nor a eukaryote.
Ans . Amoeba, being a protist, are eukaryotes.
Ans . Yeast, being fungi, is a eukaryote.
Ans . Eubacteria, or ‘true’ bacteria, are a class of bacteria and thus are prokaryotes.
Ans . E . coli, being bacteria, is a prokaryote.
Ans . Human cells have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles and thus are eukaryotes.
Ans . Euglena, being protist, are eukaryotes.
Ans . Cyanobacteria or blue-green algae lack membrane-bound organelles and well-organized nuclei and thus are prokaryotes.
Ans . Yes. Eukaryotes originated at least 2.7 billion years ago, following almost 1 to 1.5 billion years of prokaryotic evolution.
Ans . Prokaryotic protein synthesis uses 70S ribosomes in comparison to 80S ribosomes in eukaryotes. Protein synthesis in prokaryotes is a continuous process with transcription. On the other hand, in eukaryotes, protein synthesis starts after transcription is complete.
Ans . Elodea is a plant genus, and thus is a eukaryote.
Ans . Onion cells and cheek cells are eukaryotic cells because they possess membrane-bound organelles and a well-organized nucleus.
Ans . Mold, being fungi, is a eukaryote.
Ans . HIV, being a virus, is neither a prokaryote nor a eukaryote.
Ans . Streptococcus is a bacterial genus and thus is a prokaryote.
Ans . As cancer cells are found only in multicellular organisms, which are eukaryotes, they are eukaryotic cells.
Ans . All red blood cells, including rodent red blood cells, are eukaryotic because they have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Ans . Fish cells, including sharks, are eukaryotic because they have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Ans . Monera is a kingdom that includes bacteria and archaea. They have a prokaryotic cell organization.
Ans. Saccharomyces is a genus of fungi, including many yeast species. They are thus eukaryotes.
Ans. Spirillum is a bacterial genus and thus is a prokaryote.
Ans. Vibrio cholera, being bacteria, is a prokaryote.
- References Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes: What Are the Differences? – Thoughtco.com 47 Differences between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes – Microbenotes.com Prokaryotic versus Eukaryotic Cells – Ib.bioninja.com.au Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: What’s the Difference? – Livescience.com
Article was last reviewed on Monday, October 9, 2023