Cellular respiration is the process by which cells release energy by breaking down glucose molecules. It is broadly categorized into two types: aerobic and anaerobic.
What are Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
Aerobic respiration is the process through which cells break down the glucose molecule to convert its stored biochemical energy into energy-coin Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in the presence of oxygen. This type of respiration is the primary energy-yielding process of all living beings, providing all the energy to maintain life.
Anaerobic respiration, the most primitive form of respiration on earth, is how cells convert the stored energy of glucose into ATP in the absence of free oxygen. It provides energy to the cells very rapidly.
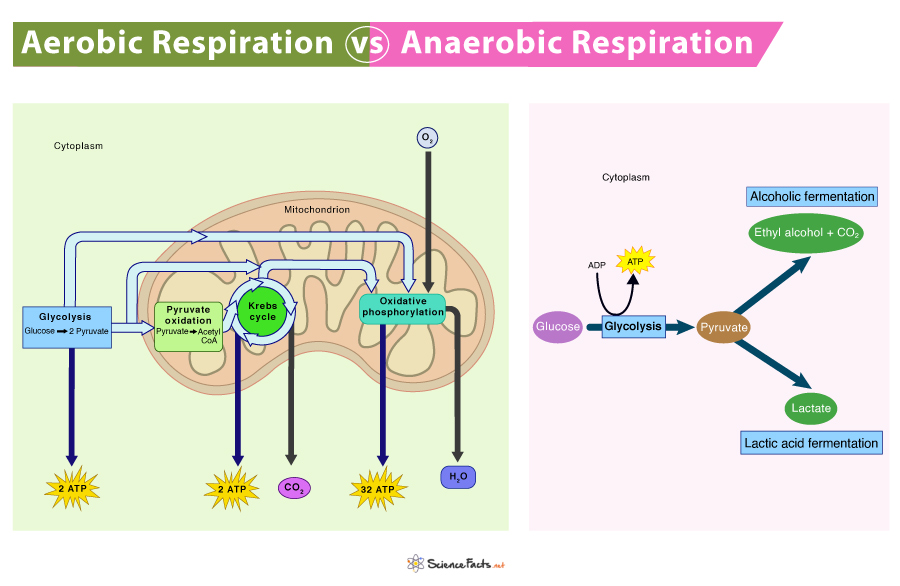
Aerobic vs Anaerobic Respiration
Compare and Contrast
As stated, both types of respiration aim to produce energy from glucose. However, two processes do not follow the same pathway and are not equivalently efficient. Although some cells may undergo just one type of respiration, most cells use both types, depending on an organism’s needs.
What is the Difference between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
Similarities
- Both oxidize similar substrate, glucose
- Both produce ATP
Ans . Both anaerobic and aerobic respirations require glucose.
Ans . Cellular respiration comprises both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Ans . In fermentation, an organic molecule, pyruvate, is used to regenerate NAD + from NADH. On the other hand, in aerobic and anaerobic respiration, glucose gets broken down in the presence and absence of oxygen, respectively, yielding ATP.
- References Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration – Ck12.org Anaerobic vs Aerobic Respiration – Bio.libretexts.org Differences Between Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration – Study.com Aerobic and anaerobic respiration – Bbc.co.uk Cellular respiration review – Khanacademy.org
Article was last reviewed on Thursday, February 2, 2023